Legg Calve Perthes Disease Dog
Legg calve perthes disease dog. With successful treatment the outlook for a dog with Legg-Perthes. Named after Arthur Legg Jacques Calve and Georg Perthes the orthopedic surgeons who in 1910 identified and studied the condition in young children Legg-Calve-Perthes Disease is an orthopedic condition that characterizes with spontaneous wasting of the femoral head. In dogs it is most often seen in the miniature and toy breeds between the ages of 4 months to a year.
Diagnosis with physical examination and medical imaging is relatively easy. A CDC Fact Sheet. Lick Granuloma in Dogs.
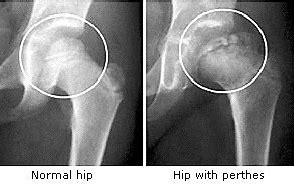
Legg-Perthes is a painful condition that causes the hip joint to crumble and collapse. However it can happen to larger dogs as well. The incidence of Legg-Calve-Perthes disease among litters with affected individuals is examined for four of the smaller breeds of dog with special regard to the West Highland white terrier and the Yorkshire terrier.
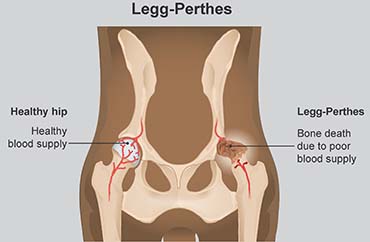
Legg-Perthes Disease in Dogs. In these two breeds the incidence is such to indicate monogenic recessive inheritance of. LCP results when the blood supply to the femoral head is interrupted resulting in avascular necrosis or the death of the bone cells.
Legg-Calve-Perthes Disease also known as LCP disease is a painful condition that tends to affect small dogs under 25 pounds. Lice in Dogs and Cats. Legg-Calve-Perthes Disease aseptic or avascular necrosis of the femoral head Avascular necrosis occurs when the bone that makes up the ball portion of the hip is damaged from lack of blood supply.
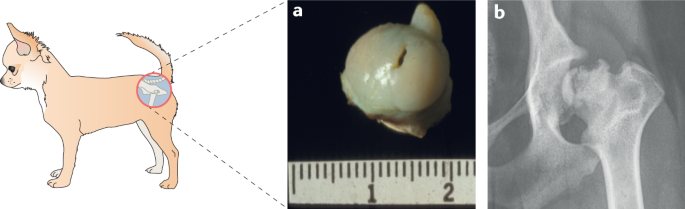
In fact as long as the degeneration is caught early and the dog is able to undergo surgery dogs suffering from this disease typically go on to live happy healthy lives without impairment. It is characterized by an ischemic necrosis of the femoral head resulting in a deformation and an incongruity of the joint. Various hypotheses exist among experts as to what causes LCP in dogs.
While the effects are concerning and severe proper care can lead to full recovery. Legg-Calve-Perthes disease causes a dog to limp on the affected leg.
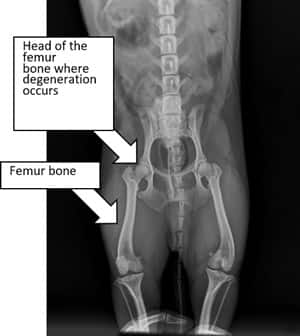
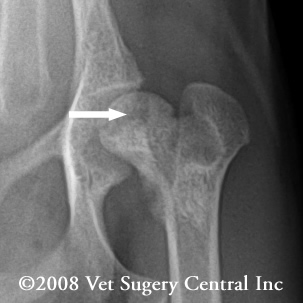
LCPD refers to the spontaneous degeneration of the femoral head the top portion of the femur leg bone.
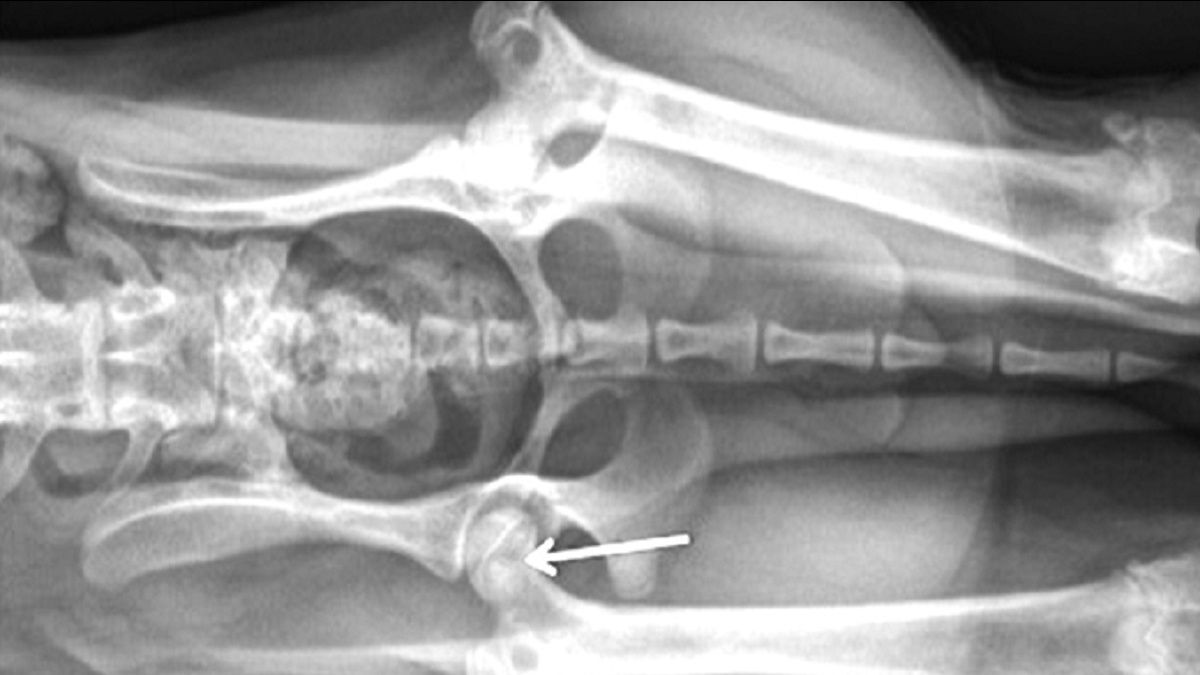
A CDC Fact Sheet. In the early stages of the disease the bony capital femoral epiphysis was necrotic but the articular cartilage and growth plate cartilage were not affected. Leptospirosis and Your Pet. However it can happen to larger dogs as well. If you notice any of the symptoms mentioned above. Legg-Perthes affects young dogs and is most common in small breeds. It is uncommon for Legg-Calve-Perthes to affect both hips an affected dog usually limps on only one rear leg. Legg Calvé Perthes disease LCPD is a developmental abnormality that usually affects young small breed dogs. With successful treatment the outlook for a dog with Legg-Perthes.
Diagnosis of Legg-Calve-Perthes Disease in Dogs. Legg-Perthes Disease in Dogs. Although the etiology is still uncertain the pathogenesis is very similar to that described in humans. Legg-Perthes Disease in dogs is a medical condition in which one of the back femurs degenerates in the hip socket. Lithotripsy in Dogs and Cats. Linear Foreign Bodies in Dogs and Cats. The femoral heads of 12 dogs with naturally occurring Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease were studied by light and electron microscopic techniques.







/GettyImages-693993226-0b8ea8a16d794265b7dba9adacb16754.jpg)





















Post a Comment for "Legg Calve Perthes Disease Dog"